Get real-time consumer, competitor and market insights with 90% AI accuracy
Unify data from 30+ channels. Unlock actionable insights and power critical business decisions with Sprinklr’s AI-first consumer intelligence suite.

Customer Feedback Analysis: 5-Step Action Plan
Having enough customer feedback is the first step to feedback management. The next step is to analyze the unstructured (comments, reviews, conversations, etc.) and structured (surveys, ratings, etc.) data to uncover your customers’ pain points, preferences, sentiments about your brand, and so on.
In this article, you will learn about the different stages and types of customer feedback analysis, with lots of tips to get started. Already have a framework? This guide can be a quick brush-up on the basics!
What is customer feedback analysis?
After your survey results are in, or you’ve gotten enough feedback on other channels, the next step is to get a summary of what customers want to say through the feedback. Is it overwhelmingly good? Is it a mixed bag of reviews? Is there a certain issue with the product?
The process of analyzing feedback from structured (surveys, interviews, analytics) and unstructured (social media, reviews, forums) sources to uncover what customers want from your business is feedback analysis.
There are many ways to analyze feedback, depending on the source, type of feedback, and your business goals. When it comes to analysis, there are two broad categories — qualitative and quantitative — and there are a variety of methods under both the categories for analysis:
1. Quantitative analysis - To measure customer satisfaction and behavior using structured data via methods like statistical analysis and scoring frameworks (NPS, CSAT, etc.)
2. Qualitative analysis - To understand the "why" behind customer behavior using unstructured data via thematic, sentiment, qualitative coding, and root-cause analytics
💰What if analyzing feedback wasn’t just reactive, but proactive?
What if you could get ahead of feedback and listen to what customers are saying — on social media, reviews, or in behavior trends — and act before things go awry?
That’s exactly what a marketing consultancy brand, Athena, does by analyzing customer feedback in real-time. They navigate crises, amplify engagement, and make data-driven decisions. The result is less than 10 minutes to report emerging issues, and 850+ topics monitored in real-time.
4 Main stages of customer feedback analysis
Feedback analysis typically follows the standard process, irrespective of your analysis method and source. The difference is in the manual efforts, where you must undertake each stage manually, versus automated workflows, where the stages are automatically handled by the platform:
Data collection
Gathering both structured (e.g., survey ratings) and unstructured (e.g., open-ended comments) data using surveys, social media, online reviews, in-app feedback pop-ups, etc. If you have a voice of the customer program, you will have a broader feedback pool to tap into for data.
Segmentation
Like every data, feedback may contain redundancies, such as irrelevant feedback, low-quality feedback, uncategorized feedback, etc.
At this stage, you are supposed to clean the raw feedback data into categories so that you can focus on analyzing the ones that are your priority. Some categories include segmenting feedback based on:
- Product or service
- Geographic location
- Customer journey
- Customer satisfaction
- Demographics
- Sentiment
- Business-specific themes
Analysis
With the clean feedback, you can now process it to gain actionable insights. You can analyze feedback qualitatively and quantitatively, with each having several methods of analysis.
For example, sentiment analysis is a popular qualitative feedback analysis method, while the NPS score is a popular quantitative direction.
Action
The next steps are prioritizing issues based on the impact and frequency of the feedback, developing specific action plans to address the issues, and delivering reports to various departments to implement changes.
👉 Related: A complete guide to customer feedback management
5 Steps to start analyzing customer feedback (+ tips)
Let’s look at the step-by-step process to get started with customer feedback analysis:
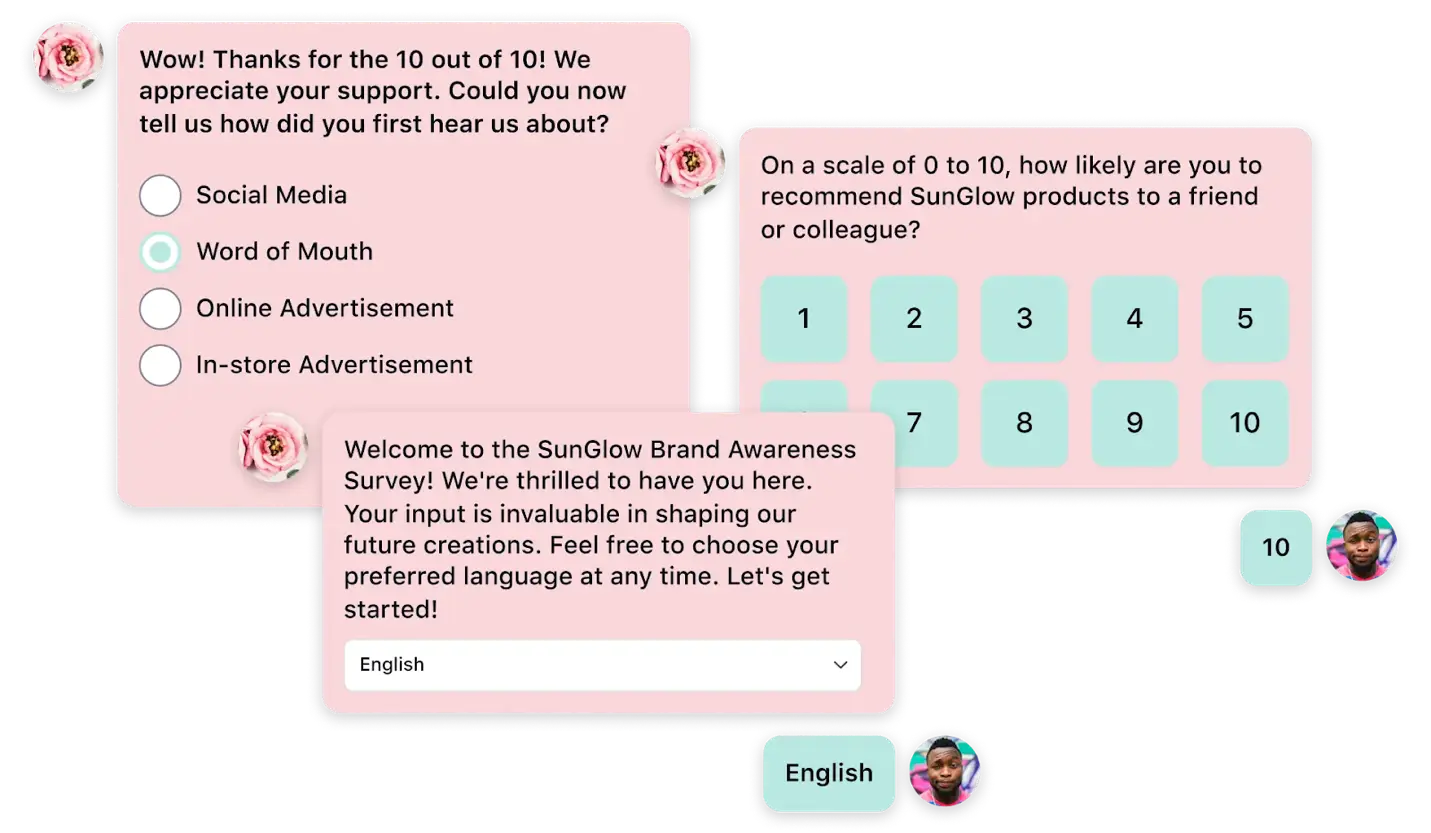
Step 1: Collect and consolidate customer feedback
Start by defining your enterprise’s primary goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs) of the feedback management effort. This is important to avoid data hoarding, ambiguous reporting, or gathering irrelevant feedback that you wouldn’t require.
Goals could look like -
- Increase the net promoter score (NPS) by 10 points within 12 months
- Improve the customer satisfaction score (CSAT) by 15% over the next fiscal year
Once the goals are set, you need a solid central data lake or warehouse to ingest the feedback into one source. It will help validate and analyze the data.
Here, you can choose to use data-gathering tools or manually export — whatever is easier for you. ✨Don’t have a feedback-collection system? Here are five ways to collect customer feedback.
Three tips to collect customer feedback
- Identify the key channels that bring in feedback, like customer surveys, social media interactions and DMs, customer service interactions, review sites, etc. Since every feedback source will not automatically lead to your central data lake, you can use APIs, and webhooks to automate the process
- For enterprise-grade data collection, use a consumer intelligence platform to automatically feed the data from sources like social media, emails, surveys, review platforms, call center logs, and chat transcripts in one place. This saves time and effort in developing systems and comes with built-in analysis, governance, and reporting features
- If you want to go beyond surveys, try social listening that can capture passive feedback from customer conversations in the public, as well as other traditional channels where surveys can’t reach, such as public forums, Reddit threads, review sites, etc.
⚡Pro tip - If surveys are your primary or a major feedback channel, and you’re struggling to manage and analyze multiple surveys manually, try using conversational surveys.
You can auto-generate and edit surveys using simple commands. The best part? Get a 360° view of customer feedback by combining survey responses with data from social and digital channels, review sites, and service interactions — in one dashboard.
Step 2: Validating and integrating multisource data
Raw data is rarely ready for direct analysis. Validating the feedback data ensures that it is accurate, reliable, and useful for your decision-making.
You can start this process by standardizing the incoming data formats (e.g., timestamp formats, language, and numerical ratings), especially when using tools like Excel or a Spreadsheet. Here are some data validation checks to explore:
- Data type - Confirming that each data field contains values of the proper type (e.g., numeric, text, date)
- Range - Ensuring numeric values fall within a predetermined acceptable range
- Duplication - Preventing duplicate records where each record is expected to be unique
- Completeness - Making sure required fields are not left blank
You can validate data either manually, using APIs, or automation to export and categorize data in your preferred platforms. Advanced consumer intelligence platforms validate the data using ML and AI.
Two tips to validate and integrate multisource data:
- Hemanand Vadivel, co-founder and CEO of Codebasics, a data skills training center, suggests having a few similar questions in the survey to observe how responses differ from the same person. “If the variance is extreme, you can remove those responses to keep the quality of responses high.”
- Muhammad Fawwad, a data engineer, suggests cross-referencing customer feedback with other data sources. “If possible, compare feedback with measurable metrics such as sales data, customer support logs, or user engagement metrics. Consistency between feedback and objective data adds credibility. It's also useful to validate feedback over time to identify patterns or changes in sentiment.”
- It is very easy to go down a rabbit hole of chasing perfection when it comes to data validation, suggests Prakash Hariharabalan, data analytics and digital transformation leader. “In my experience, it is very important not to allow perfection to become the enemy of great,” Prakash says, adding that aligning data quality thresholds is a key step.
Step 3: Analyzing the feedback
Validating customer feedback data helps identify and prioritize the most pressing feedback themes and takeaways to make tangible business improvements.
Topic detection, pattern recognition, and categorization through NLP can automatically identify the key topics and themes within customer feedback.
Analysis can help you learn what customers like and don’t like, want, and don’t want, specific product features they are talking about, service issues, pricing, and even churn, as Ditipriya Chakraborty, a business analyst, demonstrated!
Three tips to use AI and automation for feedback analysis:
- Use pre-trained text analysis models like BERT covering text classifications, question answering, machine translations, inference, and summarization. Note: These processes are resource-intensive and require developer bandwidth and training to utilize
- If resources permit, automate data collection with tools like Zapier to pull data from review sites, surveys, and ratings directly into your analytics tools, keeping in mind the need for source compatibility and tool support
- Explore qualitative data coding to assign metrics to feedback (especially if you want to focus on qualitative feedback). For example, if Yelp reviews praise a cafe but flag soaring prices, you’d lower the price score while coding the data. Initially, invest time to define the relevant scale for your metrics
⚡Pro tip - The best way to automate feedback analysis from multiple sources is by using the built-in AI and NLP capabilities of a consumer intelligence platform. These tools can pull in feedback data from your structured and unstructured channels and use built-in AI to slice and dice them into action-ready metrics and reports.
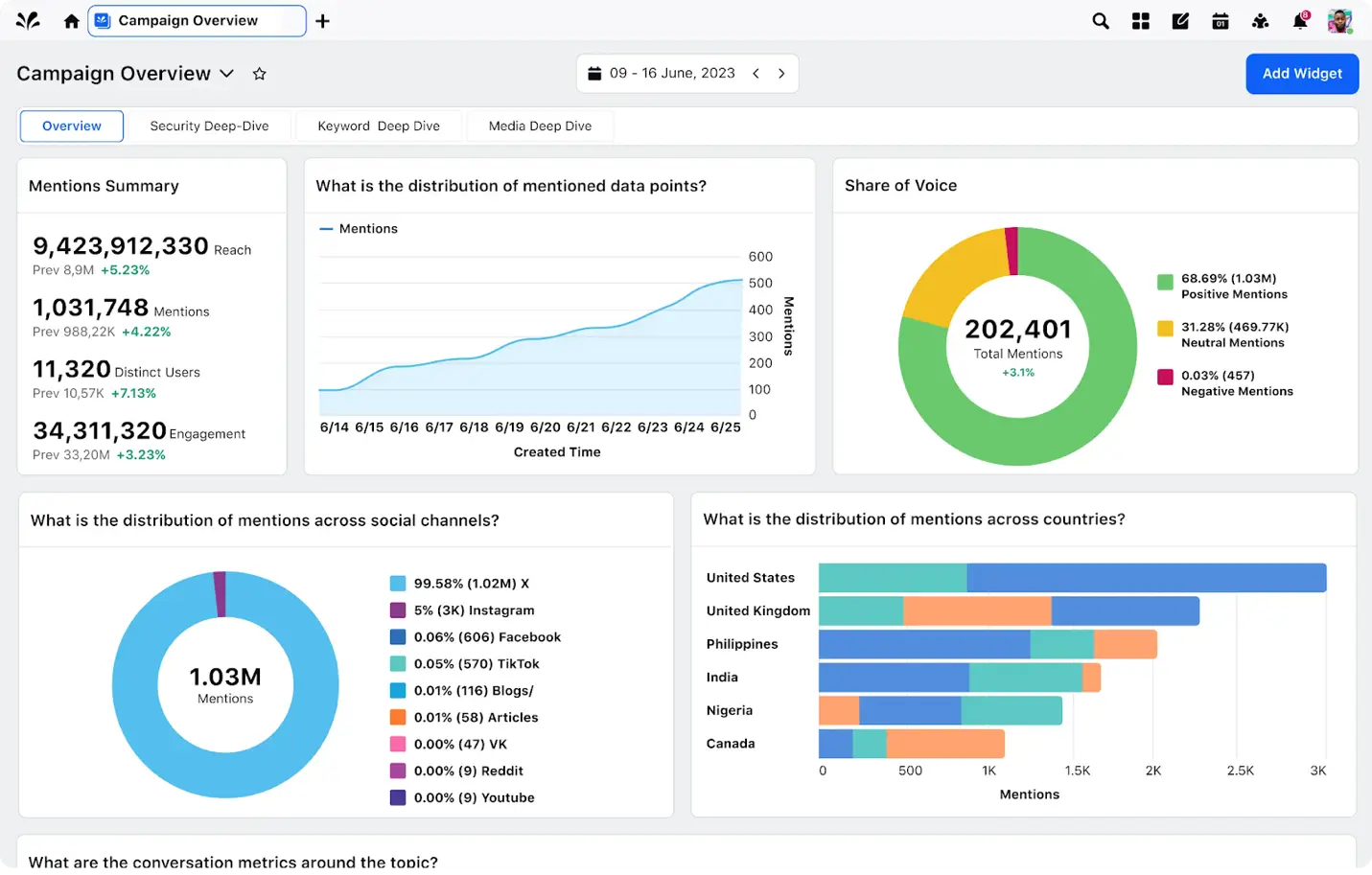
You can also broaden the scope of feedback by tapping into unconventional sources that you may not consider for analysis, such as visual assets, product, or location-specific conversations! Want to see how automated feedback analysis works in real-time?
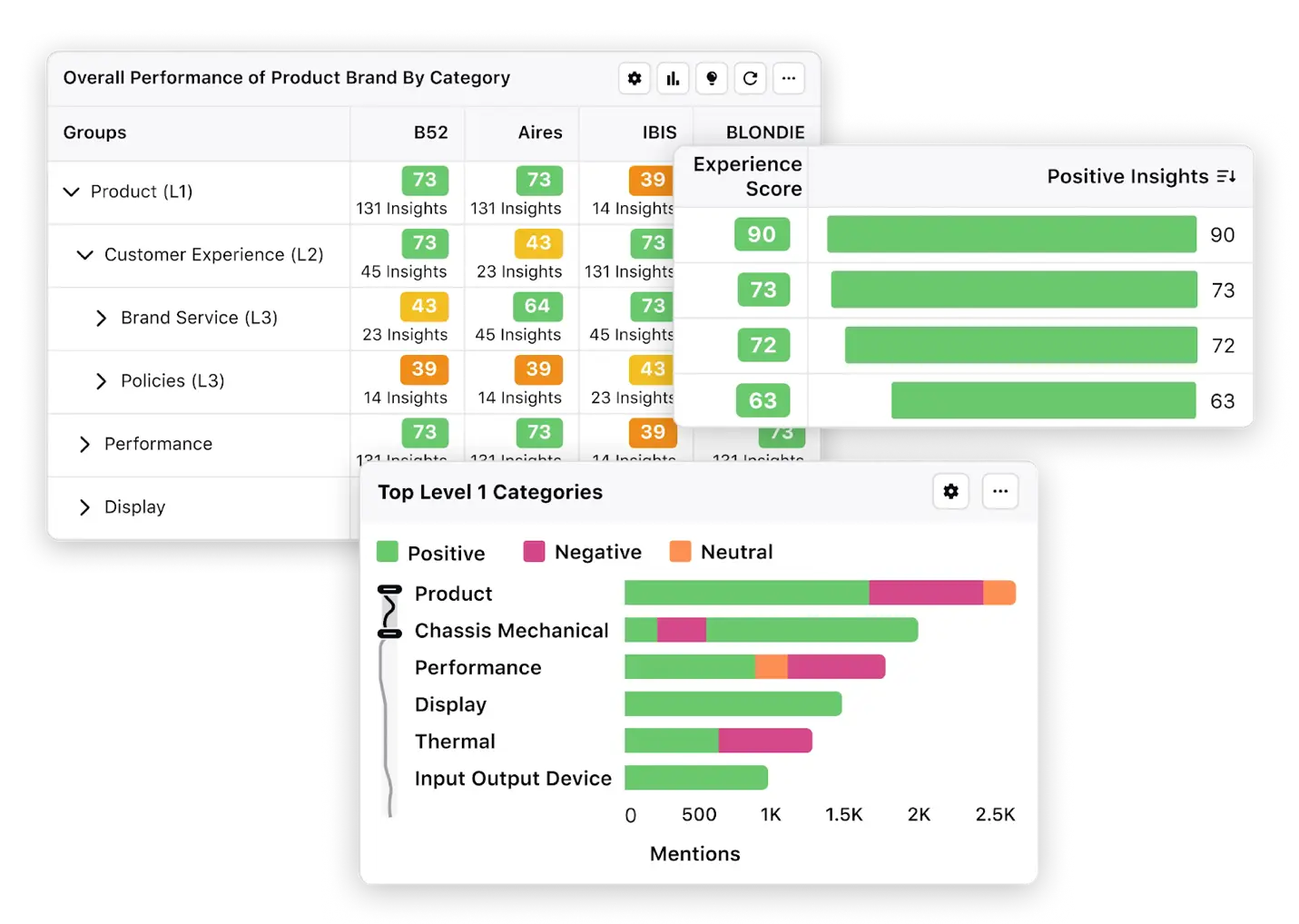
Step 4: Getting actionable insights from customer feedback
Until the third step, you were pruning and preparing the data for utility. Now, you will use the data to identify feedback that you can start to act upon.
This is the most crucial step in customer feedback analysis. The earlier steps should make this stage much easier.
Three tips to act upon customer feedback:
- Use tools like Power BI to consolidate feedback into stakeholder-prioritized buckets, adapting data depth to suit different audiences (e.g., technical dashboards for product development, social listening dashboards for marketing)
- Enhance raw data with insights — key findings, conclusions, and recommendations — that tie directly to revenue, costs, or strategic goals (e.g., lowering average hold times to potentially save $1.2M annually)
- Clarify why key feedback matters by linking themes to business objectives and KPIs, and setting target improvement rates (e.g., highlighting that a slow checkout process increases cart abandonment among e-commerce retailers)
🔥 If you use Sprinklr Insights - You can tailor the standard and custom reporting dashboards to your feedback metrics and KPIs for hyper-focused data from chosen channels. You can also schedule exports to deliver the dashboards at chosen intervals to stakeholders.
Preparing reports for team-wide dissemination of information has many benefits. However, the feedback loop isn’t complete until the implementation takes place.
Step 5: Implementing improvements and closing the feedback loop
With the customer feedback data in and analyzed, you now know what to focus on and the next steps to take.
If you have a feedback implementation system, you can get started acting upon it. At this stage, large organizations may face barriers to implementing feedback.
To avoid barriers, you need to ensure that there’s a process to use feedback to make concrete improvements.
Three tips to turn feedback into improvements:
- Assess team culture around customer feedback. Do they see it as a checkbox or a lifeline? If not, demonstrate how you'll use feedback to hit business objectives
- Assign clear ownership for translating feedback into results (e.g., “Customer success to cut onboarding complaints by 25% in Q2”) and ensure it lands with the appropriate stakeholder
- Closing the loop is important because “uncertainty over the impact of survey responses” is one of the top four reasons customers drop out of surveys, a HubSpot study found. Acknowledge your customers’ feedback right after they submit it and keep communications active throughout the feedback implementation process through emails, notifications, or newsletters
According to research, 74% of customers are more loyal when they feel heard and understood by a brand. So, proactively implementing improvements from feedback can even help reduce churn and prevent attrition.
👉 You may want to know: What is a feedback loop?
Customer feedback analysis case study, top trends, and metrics
Who’s winning with feedback management, what are others doing with it, and what metrics should you measure? Here you go:
Case study: Slack on “taking feedback any way we can…”
Slack has been consistently rated as one of the most customer-centric companies in the B2B SaaS space, and it’s reflected in its co-founder and first CEO, Stewart Butterfield’s quote from its earlier days:
“We will take user feedback any way we can get it. In the app, we include a command that people can use to send us feedback. We have a help button that people can use to submit support tickets,” Butterfield was quoted as saying by First Round.
Over the years, Slack has added several new collaboration features, such as video conferencing, screen sharing, and improved project management tools, all based on users’ suggestions.
Slack also routinely adds new integrations with apps that Slack users use more. And it seems to have worked well for the platform: A poll found that 95% of users in a survey found using an [integrated] app in Slack makes those tools more valuable.
Emerging trends and future directions in customer feedback data analysis
Here are some of the key emerging trends and future directions:
1. Businesses are moving beyond surveys: Using them as the only channel may be falling short in terms of feedback coverage, given that customers are present at touchpoints where surveys cannot reach.
Gartner predicts that by 2025, organizations with a voice of the customer program (a feedback analysis strategy) will use text and voice as feedback sources
2. Predictive analysis: Real-time feedback analysis has been a widely used tactic, but with modern listening tools and advanced AI and NLP models, data analysts are betting on predictive analytics, which considers historical data with real-time data to suggest predictions on business outcomes, patterns, trends, and insights
3. Verticalized AI: Generative AI has revolutionized data processing. Parallelly, tech organizations are also investing in verticalized AI — a subset of AI that is trained on data specific to an industry.
Platforms like Sprinklr offer verticalized AI with up to 90 %+ accuracy in discovering trends, themes, root causes, and clear actionable recommendations from feedback
4. Personalization: Personalized feedback requests based on granular insights with constant updates according to behavioral data is an emerging practice.
The next step is using these insights to deliver highly personalized experiences across all touchpoints, including customized products, services, and communications
5. Data security: Businesses are becoming more transparent about how they collect and use customer feedback data and are obtaining explicit consent from customers as a result. Protecting customer data from breaches and unauthorized access is a top priority
Customer feedback metrics to measure
When it comes to feedback measurement, quantitative feedback comes with measurable data. However, some techniques, like qualitative data coding, can help measure qualitative feedback. Here’s a list of key metrics you can measure:
Quantitative customer feedback metrics
Indicate the nature of the feedback on a linear scale, often zero to nine, with lower scores indicating a negative experience
1. NPS - Measures customer loyalty by asking them how likely they are to recommend your product or service on a scale from 0 to 10
2. CSAT - Short, direct questions after an interaction or purchase (e.g., “How satisfied were you with your experience?”) using a rating scale (e.g., 1 to 5)
3. Net Sentiment Score (NSS) - A numerical designation of the overall customer sentiment, typically available in sentiment analysis platforms like Sprinklr
4. Net Effort Score (NES) - Measures the ease of customer interaction or task completion (e.g., “How much effort did you have to exert to resolve your issue?”) on a numerical scale
5. Response and resolution time: Average time taken to respond to and resolve customer issues
6. First-contact resolution (FCR) - Percentage of customer inquiries or issues resolved on the first contact
Predictive customer feedback metrics
Uses historic and real-time feedback data to predict business outcome
7. Customer lifetime value (CLV) projections - Predicts the total revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with your business. Positive metrics in the corresponding data could indicate a higher CLV
8. Customer retention rate (CRR) projections - Measures the percentage of customers who remain loyal to a brand or service over a specific period
9. Churn and retention predictions - How many customers are leaving or staying, which can be influenced by their satisfaction levels
Qualitative customer feedback is expressive and detailed, with no quantifiable metrics readily attached. You must set quantification measures and analyze feedback to process further.
Make the most of customer feedback analysis with Sprinklr Insights
This five-step action plan provides a roadmap for enterprises to collect, analyze, and leverage customer feedback effectively. Whether you’re investing in in-house workflows to analyze feedback or in customer intelligence tools, the aim is to have a system in place where stakeholders can get insights from feedback and know what to act upon and how.
If you want to bring your customer feedback channels into one unified platform for better reviewing, accurate AI insights, and reporting, book a demo to see how Sprinklr Insights can help you analyze customer feedback with more efficiency!
Frequently Asked Questions
It reduces manual effort, accelerates processing, and enables faster, data-driven decisions, freeing up resources for strategic initiatives. Automated analysis also allows enterprises to modify and adjust their policies and practices by tracking customer feedback in near real-time.
They centralize data from various sources into a unified platform, standardizing it for effective analysis and a holistic customer view. These tools also help you distinguish between insightful and non-insightful data, which can help you refine your business policies.
It identifies user needs and pain points, enabling you to optimize digital platforms, enhance user experience, and drive digital adoption. You can track the positive and negative aspects of your products and services and make changes as needed by utilizing sentiment analysis and social listening tools.
Yes, by using clean, representative data, employing diverse analysis techniques, and being aware of potential biases in data collection and interpretation. You should also invest in data validation and integration processes to ensure high standards of accuracy and reliability.
Integrating and handling large volumes of unstructured data and ensuring data quality and consistency across the enterprise is one of the biggest challenges when implementing customer feedback analysis at scale. Another challenge enterprises face is low customer participation due to survey fatigue, unclear incentives for participation, and excessive requests for feedback.

