Understanding Smart Routing
Updated
AI-powered Smart Routing leverages available customer data for better mapping of unassigned cases to appropriate agents. Sprinklr’s Smart Routing feature is designed to connect your customers with care agents that are best suited for them leading to optimal outcomes with customers' queries getting resolved quickly and overall improved care KPIs performance.
Smart Assignment uses data from past interactions to dynamically match customers to agents using proficiency in solving the incoming intent, perceived service quality, and other strategies leveraging CSAT and NPS.
Note: Access to this feature is controlled by SMART_ASSIGNMENT_ADVANCED_UI_CONFIGURATION_ENABLED dynamic property. To enable this feature in your environment, reach out to your Success Manager. Alternatively, you can submit a request at tickets@sprinklr.com.
Problem Statement
In standard pairing strategies, the decision about which agent will take care of an inbound message, mainly rely on the agent's capacity, availability, priority, and basic skills (associated via Sprinklr Assignment Engine/Unified Routing). However, these strategies are suboptimal because
Skills are manually assigned and usually not frequently updated.
Performances of agents on other important customer perceived aspects, e.g., communication proficiency, patience, etc., are not taken into account.
Demographic, behavioral, psychographic data about agents and customers, if available, is not taken into account.
Important Pre-requisites
Before we start implementing smart routing, it's important to ensure that we have the necessary pre-requisites in place which are discussed below :
Issue Intents: To get started, we identify the different types of issues or inquiries your customers commonly have. These could include issues like "Repair," "Refund," "Technical Support," and more. Each issue intent should represent a specific category of customer inquiries that require expertise to handle effectively.
Coverage and Case Diversity: For increasing the effectiveness of Smart Routing, we have to ensure that there is a wide coverage of inbound cases in the platform that correspond to the identified issue intents. This diversity of cases helps the algorithm learn and make informed decisions when matching cases to agents.
Sufficient Case Data: For each issue intent, we gather a substantial number of historical cases. It's recommended to have at least 100 cases for each intent. These cases will serve as the foundation for training the smart routing algorithm and improving its accuracy over time.
Survey Scores and Agent Feedback: Next, we collect customer survey scores such as Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) ratings. These scores provide valuable insights into customer satisfaction and the performance of agents. Additionally, any feedback or scores related to agent performance can be used like predicted CSAT, or partner-specific metrics that can help assess the agent's capabilities.
Agent Pool Availability: Apart from covering cases, we should also have a sizable pool of agents available in the queue where smart routing will be implemented. Having a diverse group of agents allows the algorithm to make informed decisions and optimize case assignments based on agent expertise and availability.
How Smart Routing finds the best agent
After we ensure that the above pre-requisites are met for a queue, the routing system finds the best suitable agent by:
Step 1: Data Collection and Score Calculation
Calculate Weighted Average Scores: Calculating weighted average scores for agents across individual intents and at an aggregate level using historical case data. This involves assessing agent proficiency in solving issues, perceived service quality, and other relevant criteria.
Automatic Training Job: Setting up an automatic training job to continuously update and refine the agent scores. You can choose the frequency of training updates, such as hourly, daily, or weekly, depending on your needs.
Step 2: Agent Ranking
Agent Ranking: Assigning a rank to each agent based on the above calculated scores. The lower the rank, the better the agent's suitability for handling cases.
Available Agent Selection: When an incoming case needs to be routed via smart routing, the algorithm selects the best-ranking (lowest rank) agent who is also available at the time of assignment.
Step 3: Fine-Tuning and Customization
Configuration Options: Admins can explore various configuration options to fine-tune the scoring algorithm according to specific business requirements. For instance, they can set thresholds for the number of cases an agent should handle before being considered for smart routing.
Impact Measurement
CSAT Analysis for Smart Routing Cases:
We use care reporting module to visualize the impact of enabling smart routing. For example, we can compare CSAT scores before and after implementing smart routing to assess the effect of smart routing on customer satisfaction.
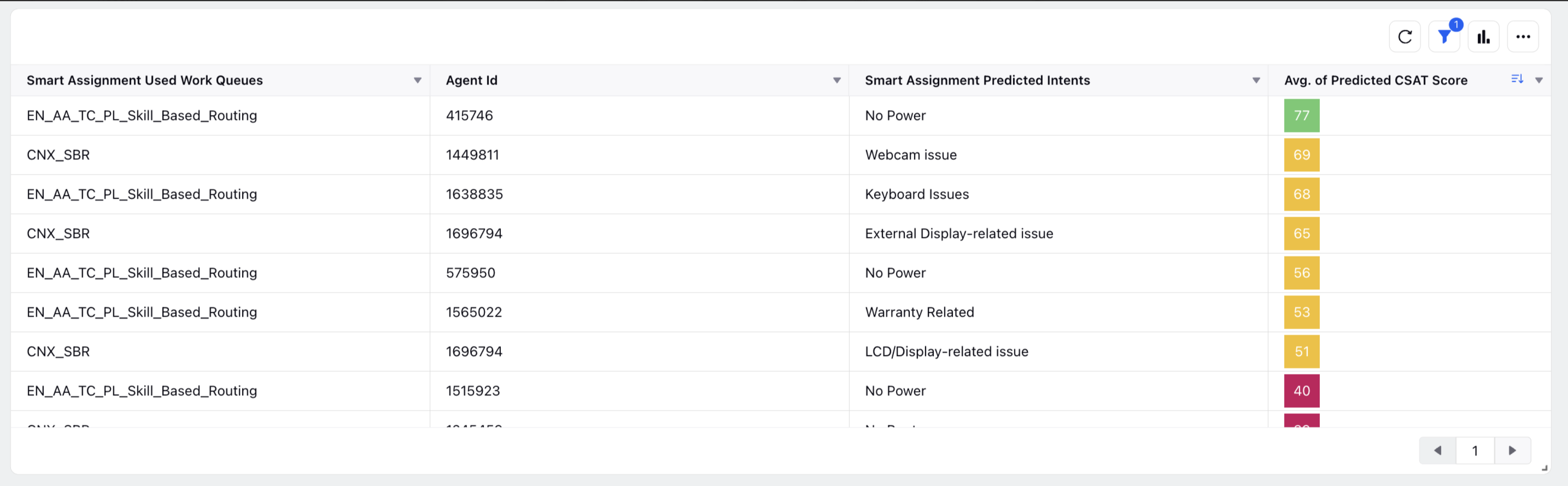
Transperancy of Agent Scores using reporting:
Admins can access historical and current agent scores for specific intents through reporting Dashboard. This allows for better tracking of agent performance and ranking over time.
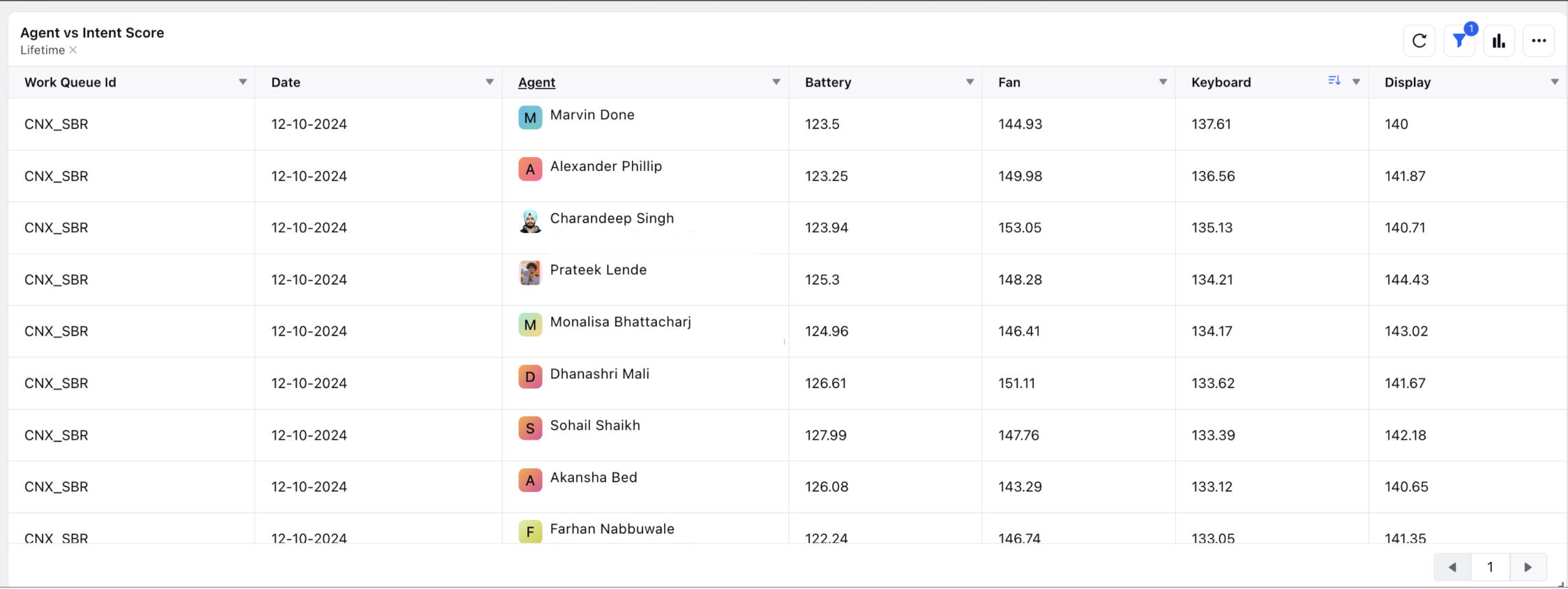
.