How are Contact Driver Insights Generated?
Updated
The Contact Drivers Gap Analysis aims to ensure comprehensive coverage and effectiveness of the configured Contact Drivers by addressing missing drivers, incorporating new ones as needed, and refining existing guidelines based on insights from contact center interactions. This involves several key aspects:
1. Identification of Missing Contact Drivers:
This entails identifying any Contact Drivers that are not currently configured but are necessary for analyzing customer cases effectively. These missing contact drivers may be crucial for understanding and categorizing incoming customer inquiries.
2. Relevance of Contact Drivers:
Additionally, the analysis includes identifying new contact drivers that were not initially considered relevant during the configuration of the Contact Drivers model. However, with the emergence of new cases, these Contact Drivers have become important and must be integrated into the system for accurate case analysis.
3. Evaluation of Existing Contact Driver Guidelines:
The analysis also assesses any gaps in the guidelines of the existing Contact Drivers. This evaluation is based on insights gathered from contact center conversations. If these conversations reveal the need for updates to the guidelines to address overlaps or address any missing aspects, adjustments can be made accordingly.
Note: The Contact Drivers gap analysis is a feature with limited availability.
Generating Contact Driver Insights
The generation of Contact Drivers Insights involves a multi-step process aimed at identifying areas for the creation of new Contact Drivers or updates to existing ones based on customer cases. Below is a detailed explanation of each step:
Step 1: Perform Case Analysis
Granular analysis is conducted for individual customer cases to understand the specific issues they encountered.
The focus is on understanding the most granular Contact Drivers of the conversation, irrespective of the existing list.
Step 2: Validate Existing Contact Drivers
In this step, the identified Contact Drivers is verified against the current list of configured Contact Drivers at the most granular level.
If the contact driver exists:
The need for a guideline change is determined, and the guideline change is suggested if necessary.
If the indentified Contact Drivers is new:
Its parent Contact Drivers is determined. For example, if L3 is missing, its parent L2 is identified.
The presence of the parent L2 in the current list of contact drivers is checked.
If it is present, the suggestion is made to create the new Contact Drivers within this L2, along with the guideline it should follow.
If it's not present, the process is repeated to determine its parent Contact Drivers (L1).
The presence of the new parent contact driver (L1) in the configured list of Contact Drivers is checked.
If it is present, the suggestion is made to create the new identified Contact Drivers and L2 within this L1, along with the guidelines it should follow.
If it's not present, the suggestion is made to create L1 as well. This process continues until the top level is reached.
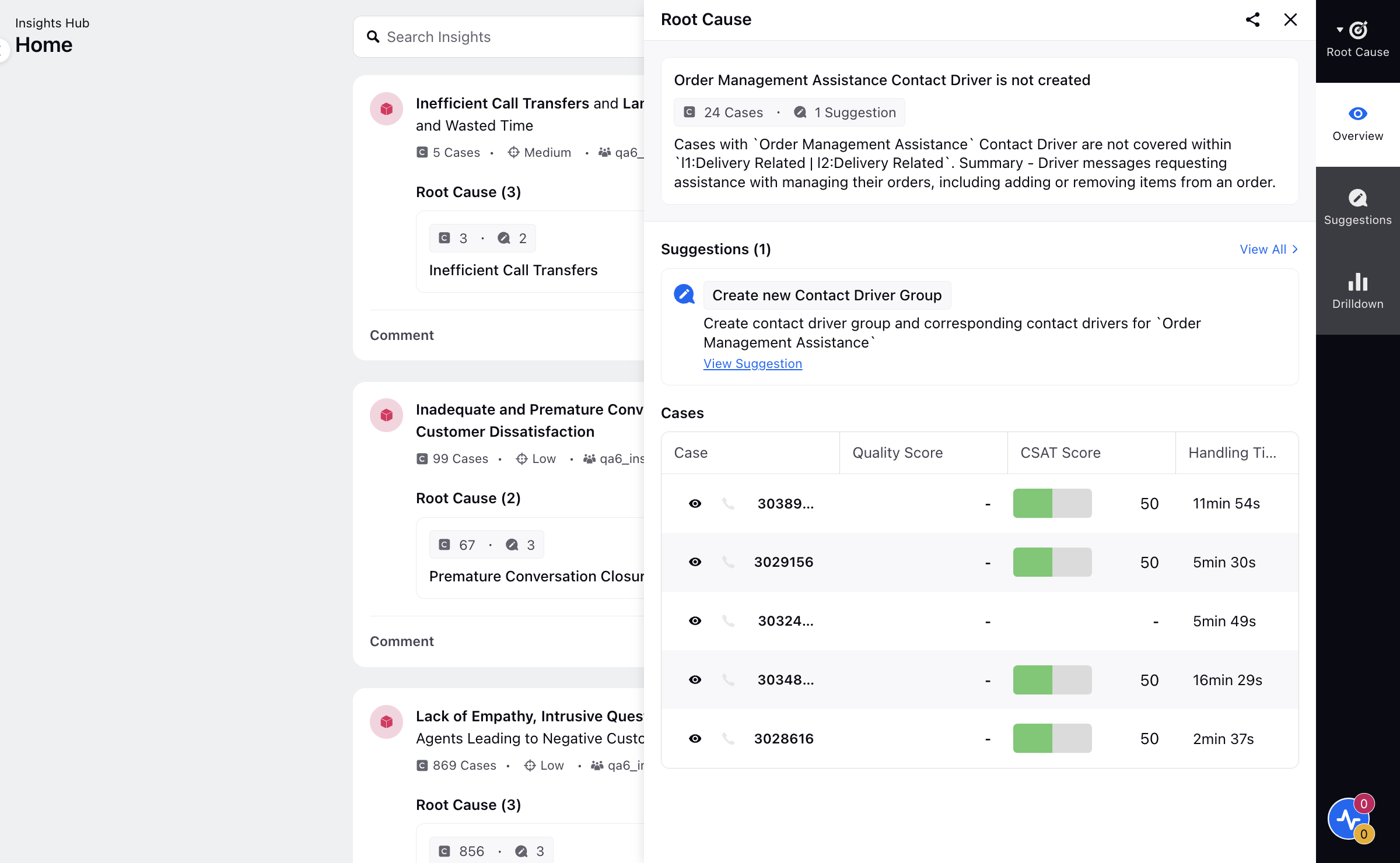
This comprehensive approach ensures that all customer cases are thoroughly analyzed to identify the need for new Contact Drivers or updates to existing ones, ultimately improving the effectiveness of the Contact Drivers model.